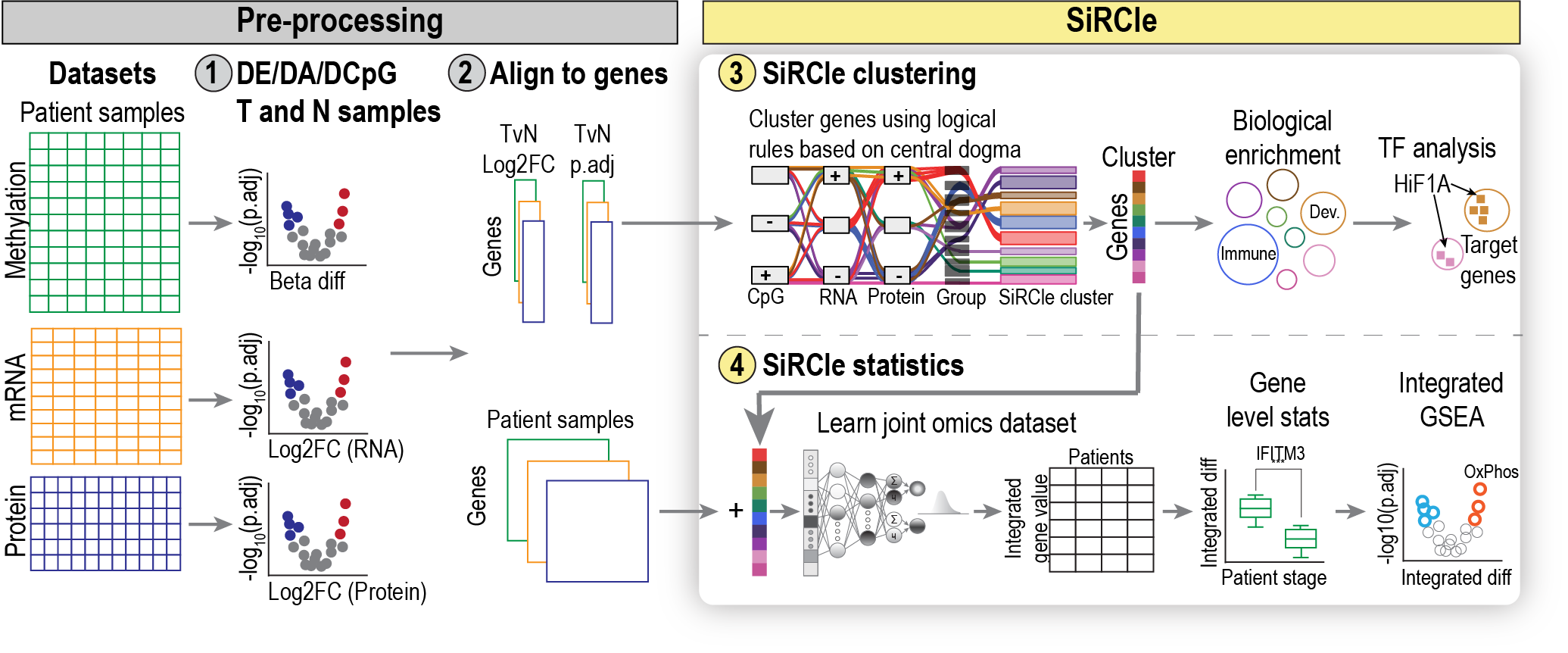
SiRCle (Signature Regulatory Clustering) model integration reveals mechanisms of phenotype regulation in renal cancer¶
Information¶
This site hosts the information associated with the paper: SiRCle (Signature Regulatory Clustering) model integration reveals mechanisms of phenotype regulation in renal cancer. Here we provide the code and data used for all the analyses in the paper and link to the packages we developed as part of producing the paper.
Links to analyses and data¶
Places where this (or a package we developed for this) has been presented¶
Date |
Conference |
Type |
|---|---|---|
28 April 2021 |
Melbourne bioinformatics seminar series |
Presentation |
25 May 2021 |
Poster |
|
15 - 17 Sep 2021 |
Short talk |
|
15 Jan 2022 |
Multi-Omics ONLINE - Webinar 2: Data integration and interpretation to unveil novel insights |
Talk |
Authors¶
Ariane Mora^1, Christina Schmidt^2,3, Brad Balderson1, Christian Frezza3#, Mikael Bodén1#
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences, University of Queensland, Molecular Biosciences Building 76, St Lucia QLD 4072, Australia.
Medical Research Council Cancer Unit, University of Cambridge, Hutchison/MRC Research Centre, Box 197, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Cambridge CB2 0X2, United Kingdom
CECAD Research Center, University Hospital Cologne, Joseph-Stelzmann-Str. 26, 50931 Cologne, Germany
^Joint first authors equally contributed; the order is interchangeable and up to the authors discretion #Joint last authors
Note Christina and Ariane are equal joint first authors and the authors may swap the order of their names as they so choose :)
Abstract¶
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) tumours develop and progress via complex remodelling of the kidney epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome. Given the subsequent tumour and inter-patient heterogeneity, drug-based treatments report limited success, calling for multi-omics studies to extract regulatory relationships, and ultimately, to develop targeted therapies. However, current methods are unable to extract nonlinear multi-omics perturbations.
Here, we present SiRCle (Signature Regulatory Clustering), a novel method to integrate DNA methylation, RNA-seq and proteomics data. Applying SiRCle to a case study of ccRCC, we disentangle the layer (DNA methylation, transcription and/or translation) where dysregulation first occurs and find the primary biological processes altered. Next, we detect regulatory differences between patient subsets by using a variational autoencoder to integrate omics’ data followed by statistical comparisons on the integrated space. In ccRCC patients, SiRCle allows to identify metabolic enzymes and cell-type-specific markers associated with survival along with the likely molecular driver behind the gene’s perturbations.
Getting in touch¶
Please contact CS (christina.schmidt@uni-koeln.de), and AM (uqamora@uq.edu.au)
Citing the preprint¶
Link to preprint
Package info
Reproducibility
- Notebook for RNA processing part 1
- Notebook for Clinical processing
- Protein Imputation
- Notebook for Protein processing
- Notebook for Methylation processing
- Notebook for Phospho-proteoimcs peptide processing
- Notebook for RNA processing part 2
- Notebook for Generating datasets
- Tumour vs normal comparison
- Notebook for Filtering CpGs to Genes
- Notebook for performing SiRCle clustering
- ORA for SiRCle clusters
- Notebook for Over Representation Analysis Visualisation for SiRCle
- Notebook for TF analysis
- Notebook for VAE integration
- GSEA on the integrated VAE value
- Set up single cell files
- Notebook for Single cell analysis using integrated genes Stage IV vs Stage I
- Notebook for Single cell analysis using integrated genes for PBRM1 vs BAP1
- Notebook for metabolomics analysis using publicly available data
- Notebook for RCM data with metabolic pathways
- Notebook for VAE data with metabolic pathways
- Notebook for MOMIX benchmarking
About